Tags
DEPOSITION OF IRON, DISSOLUTION OF IRON, ELECTRONATION OF O2, ELETROCHEMICAL KINETIC PARAMETERS, EVULUTION OF HYDROGEN, OXYGEN EVOLUTION, REDUCTION OF I3-
5.1. ELETROCHEMICAL KINETIC PARAMETERS
The following parameters must be determined for determining the required kinetic parameters.
- Overall reaction
- Entities in solution
- Surface coverage
- Reaction order
- Rate is a function of applied potential. Hence, plot of lni vs η will give io from intercept & symmetry factor, β or transfer coefficient, α from the slope.
- Rate of an electrochemical reaction refers to the evaluation of io and the symmetry factors or the transfer coefficients for the electrode process.
- An electrode is perturbed from its equilibrium state by over potential and the net reaction is determined as a function of i, which is similar to change of concentration at equilibrium and studying the rate of the fast reaction.
- Thus io refers to rate at equilibrium and the symmetry factor or the transfer coefficients convey message regarding the symmetry of the energy profile curve with respect to the reactants and the products.
The file in the LINK-1 gives an account of the concepts mentioned above
LINK-1:5.1. Electrochem Kinet Parameters
5.2: REDUCTION OF I3–
I–3 + 2e ⇒ 3I–
The reaction mechanism for the reduction of I–3 to 3I – involves three step process as shown below:
K1
I3– ↔ I2 + I– …………(1)
K2
I2 ↔ 2I ……………(2)
K3
2(I +e ⇔ I– ) …….…..(3) rds
Hence, this system is taken as a model for the study of electrode kinetics involving both electrochemical & chemical steps.
The kinetic treatment of the above reaction mechanism is shown in LINK-2 given below:
LINK-2:5.2-Rdn of I- to I3-
5.3: DISSOLUTION OF IRON
Corrosion is oxidation of metal. Corrosion of metal, in particular rusting of iron, is major technical issue. This can be treated as chemical & electrochemical process. Corrosion of iron is called rusting. 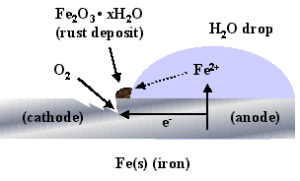
Electrochemically, rusting is oxidation of Fe into Fe2+ (dissolution of iron).The electrochemical treatment of this process is explained in LINK-3
LINK-3:5.3-Disolution of Iron
5.4: DEPOSITION OF IRON
The reverse process of rusting of iron (deposition of Fe from Fe2+) has been studied extensively as an electrochemical reaction as explained in LINK-4.
LINK-4:5.4-Deposition of Iron
5.5 (a). OXYGEN EVOLUTION
The technical importance of evolution of oxygen has been studied extensively as it is directly related to electrolysis of water. The electrochemical aspects of this process is discussed in the file attached in LINK-5(a)
LINK-5(a): 5.5(a)-Oxy Evol
5.5(b): ELECTRONATION OF O2
The cathodic process of electronation of O2 (reduction of oxygen) is linked with the anodic process of corrosion of metals.The file in the LINK-5(b) gives some electrochemical aspects of this process.
LINK-5(b): 5.5(b)-Elect of Oxy
5.6: EVULUTION OF HYDROGEN
The importance of evolution of hydrogen has been studied extensively as it is directly related to electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen. The electrochemical aspects of this process is discussed in the file attached in LINK-6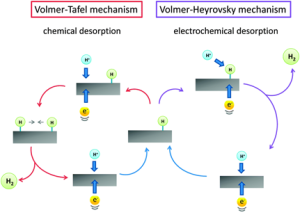 LINK-6: 5.6-H2 Evol
LINK-6: 5.6-H2 Evol
&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&
Please go to CONTENTS for all the Articles in PoC: Click below
https://dradchem.wordpress.com/2015/06/22/properties-of-chemistry-poc-contents-2/
Pingback: PROPERTIES OF CHEMISTRY (PoC): Contents | PROPERTIES OF CHEMISTRY(PoC)